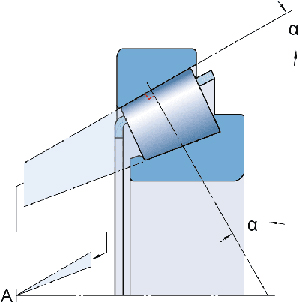
Tapered roller bearings are designed to accommodate combined loads, that is, radial and axial loads acting simultaneously. The extension line of the raceway intersects at the same point on the bearing axis, to achieve true rolling, so it has a low friction torque during operation. The axial load capacity of tapered roller bearings increases as the contact angle α increases. The size of the contact angle (usually 10° to 30°) is related to the calculation coefficient e (according to the data sheet): the greater the value of e, the greater the contact angle.
Features and advantages
Low friction
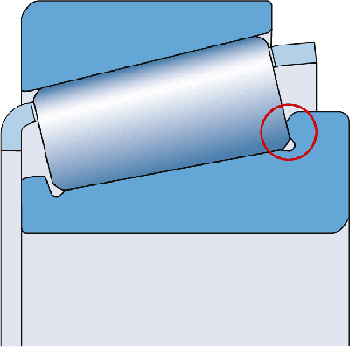
The optimized roller design on the rib and the surface finish of the rib can promote the formation of a lubricant film, thereby reducing friction. This also reduces the heat generated by friction and the wear of the ribs. In addition, the bearing can better maintain the preload and reduce the noise level during operation.
long lasting
The basic design of the bearing The shape of the logarithmic raceway of the bearing and the convex raceway can optimize the load distribution along the contact surface, reduce the stress peak at the end of the roller , and reduce the sensitivity to misalignment and shaft deflection. Straight line.
Consistency of roller profile and size
The manufacturing tolerances and dimensional accuracy of the rollers integrated in tapered roller bearings are so precise that they are almost identical. This provides the best load distribution to reduce noise and vibration levels, and enables more precise preloading.
Rigid bearing applications
A single-row tapered roller bearing usually needs to be adjusted together with another tapered roller bearing. By applying preload, rigid bearing applications can be realized.
Running-in phase with a drop in peak temperature